An American study has warned that excessive intake of fats and sugars can increase the risk of liver cancer, by destroying DNA in liver cells.
Cellular aging
Researchers from the University of California explained in the study, the results of which were published on Friday in the journal Nature, that this system promotes the occurrence of a pathological condition called “fatty liver inflammation associated with metabolic dysfunction (MASH)”, a condition that leads to cell damage, and stimulates its entry into a state of cellular aging.
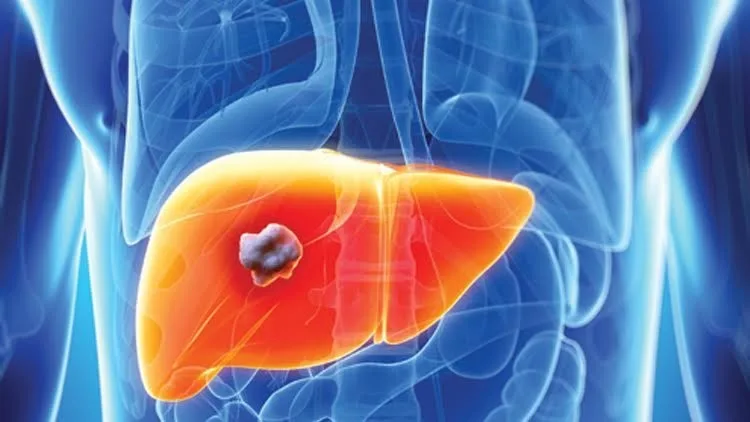
Increased incidence of injury
According to the study, recent years have seen an increase of up to 25-30 percent in the incidence of liver cancer, with most of this increase associated with the prevalence of fatty liver disease, which currently affects 25 percent of adults in America. Many of these patients suffer from a severe form of the disease called “fatty hepatosis with metabolic dysfunction”, which increases the risk of developing the disease.
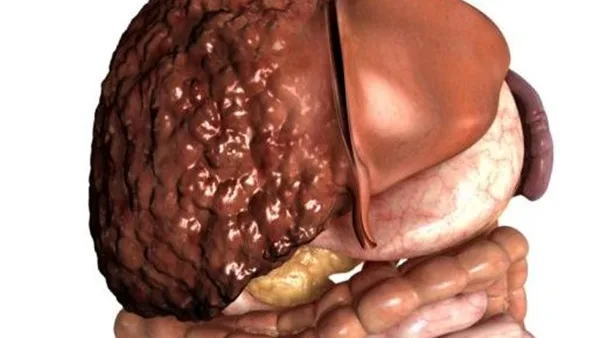
The effect of fats and sugars on cellular stress
By studying human cells, researchers have discovered that a diet rich in fat and sugar, such as fast food, sweets, carbonated drinks, and processed foods, leads to DNA damage in liver cells, and this condition is a natural response to cellular stress; cells stop dividing but remain metabolically active.
However, the team found that some damaged cells that have entered a state of cellular aging do not die; they remain a “time bomb”, and they can start multiplying again at any time, eventually leading to their transformation into cancer cells.
Comprehensive genomic analyses of DNA in tumors have also shown that cancerous tumors arise from liver cells damaged by the disease “fatty hepatitis associated with metabolic dysfunction”, highlighting the direct relationship between the diet causing genetic damage and the development of cancer.
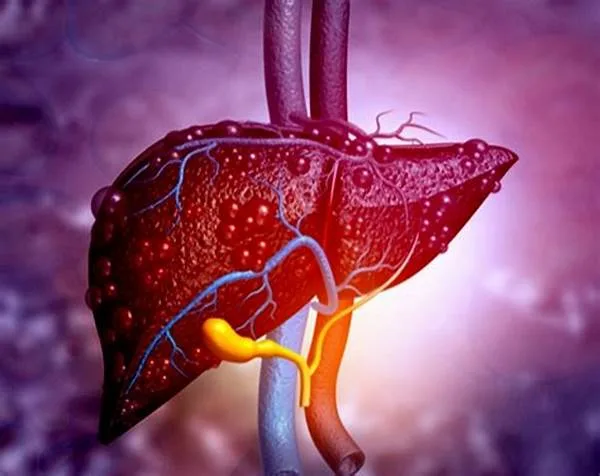
The importance of diet risk awareness
The researchers noted that these results suggest that the treatment of DNA damage caused by a poor diet may be a promising path in the Prevention of liver cancer.
Understanding the effect of diet on DNA also contributes to the development of new therapeutic strategies to combat cancer.
The team stressed the importance of raising awareness of the dangers of a poor diet, which includes foods high in fat and sugar, as this system not only affects physical appearance and increases the incidence of obesity, but also causes damage to cells and DNA, increasing the need to improve dietary habits as a means of preventing cancer and liver disease.
It is noteworthy that liver cancer is among the most common cancers in the world, and it is often associated with chronic diseases, such as viral hepatitis “C” and”B”, as well as fatty liver disease.
