A groundbreaking study released by the United Nations’ International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has found a significant link between consuming alcoholic drinks, particularly beer and spirits, and an increased risk of pancreatic cancer. The research, which analyzed data from over 120,000 participants across several countries, provides further evidence of the devastating health impacts of excessive alcohol consumption.
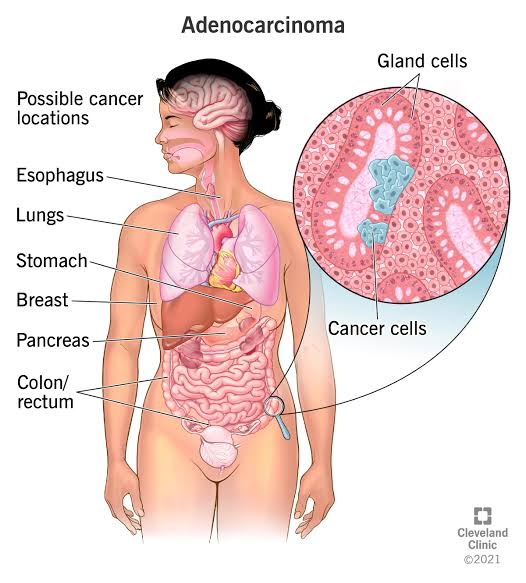
According to the study, individuals who consume high amounts of alcohol, especially beer and spirits, are at a significantly higher risk of developing pancreatic cancer compared to those who drink moderately or abstain altogether. The risk is particularly pronounced for heavy drinkers, with the study suggesting that consuming more than three drinks per day can increase the risk of pancreatic cancer by up to 40%.
Pancreatic cancer is one of the deadliest forms of cancer, with a five-year survival rate of just 9% in the United States, according to the American Cancer Society. The disease often goes undiagnosed until its advanced stages, making it challenging to treat effectively.
“The findings of this study are a stark reminder of the dangers of excessive alcohol consumption,” said Dr. Christopher Wild, director of the IARC. “As we continue to learn more about the link between alcohol and cancer, it’s clear that reducing alcohol intake can have significant health benefits.”
The study’s authors suggest that the increased risk of pancreatic cancer associated with alcohol consumption may be due to several factors, including:
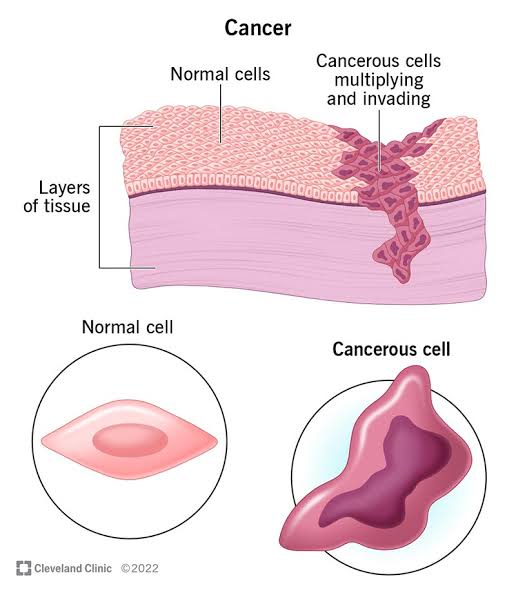
1. *Toxic compounds in alcohol:
Alcohol contains toxic compounds like acetaldehyde, which can damage DNA and increase cancer risk.
2. *Inflammation:*
Chronic inflammation caused by excessive alcohol consumption can lead to genetic mutations and cancer development.
3. *Impaired pancreatic function:*
Alcohol can impair pancreatic function, increasing the risk of cancer.
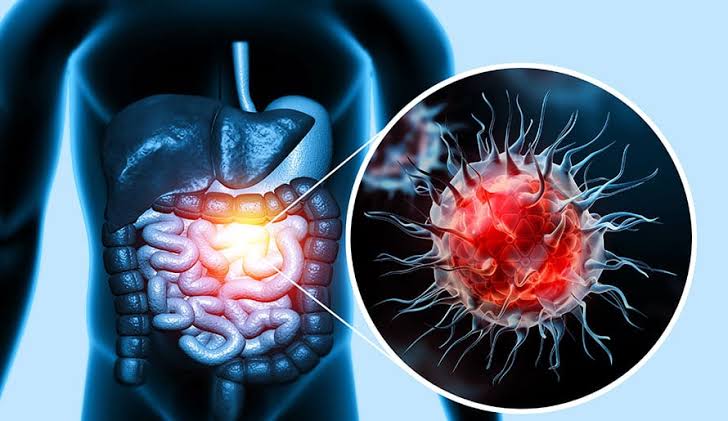
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that adults limit their daily alcohol intake to a maximum of two drinks for men and one drink for women. However, the new study suggests that even moderate drinking may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer.
*Global Impact:*
– Pancreatic cancer is the 12th most common cancer worldwide, accounting for 2-3% of all cancer diagnoses.
– The incidence of pancreatic cancer is highest in developed countries, with North America and Europe reporting the highest rates.
– Lifestyle factors, including diet and alcohol consumption, are thought to play a significant role in the development of pancreatic cancer.
*Prevention Strategies:*
– *Reduce alcohol intake:*
Limiting alcohol consumption can help reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer.
– *Maintain a healthy weight:* Excess weight and obesity are linked to an increased risk of pancreatic cancer.
– *Eat a balanced diet:*
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce cancer risk.
*What’s Next:*
The new study’s findings are likely to spark further debate about the risks and benefits of alcohol consumption. As researchers continue to explore the link between alcohol and cancer, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk by limiting their alcohol intake and adopting a healthier lifestyle.
